Ergonomic Gudeline
Ergonomics Guideline
People spend one third of their professional lives sitting on their work chairs. Anyone who performs strenuous or repetitive tasks in the workplace needs a chair that will provide them with proper support. ErgoRap® ergonomic chairs can adapt to any working situation and provide excellent stability and support, yet they do not restrict freedom of movement. Frequently changing your posture while seated reduces, unhealthy strain on the muscles and the intervertebral discs. The spinal column assumes its natural S-shape and takes the strain off the intervertebral discs and the buttocks, which improves blood circulation and the supply of nutrients. This enables the intervertebral discs to regenerate while simultaneously boosting concentration and performance.
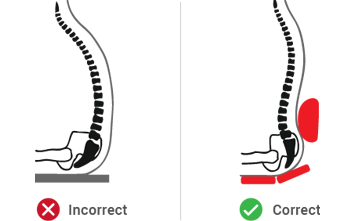
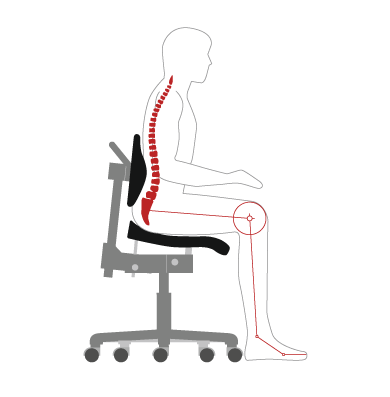
Forward posture
- The back is extremely rounded or – if the posture is rigid –pushed forward considerably.
- The center of gravity of the torso is in front of the buttocks.
- The hip angle or sitting angle is less than 90° with the thighs almost horizontal.
- Increased internal stomach pressure has an adverse effect on the venous returns in the pelvic region and results in statically tense muscles.
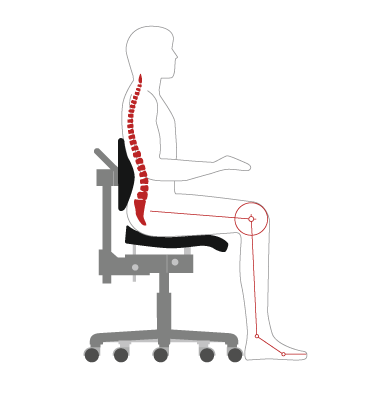
Straight posture
- The center of gravity of the torso is in the buttock area
- Statically balanced posture while seated, the spine is only slightly curved from the lumbar to the cervical spine with most of the muscles relaxed and deeper breathing.

Rear posture
- If there is a lack of support, the pelvis is turned back on the seat
- Open hip angle (in relation to the pelvis), i.e. greater than 90°
- Different spine curvature depending on the position of the sacrum.

